| Bhutan's
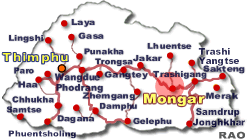
Tourist Destinations |
 |
Bhutan's Tourism Destinations |
 |
Bhutan Information |
|
|
 |
|
Thrumshingla
National Park
|
| Thrumshingla
National Park provides CGI roofs to protect ecosystem |
 |
 |
|
The Thrumshingla
National Park, spanning across Bumthang, Mongar, Lhuentse and Zhemgang,
is home to the endangered red panda, satyr tragopan, and some bird species
which have become extinct elsewhere in the world.
However,
their habitat is being threatened by human activities in the park region. Every
year hundreds of fir trees, the predominant vegetation in the area, are
being felled for roof shingles, other house construction materials and
fuel wood.
|
|
To stop the destruction of the habitat the park has provided
subsidized CGI roofs to all the 20 households of Sengor, a village which
is located at the centre of the park.
According
to the park manager, all villages within the park territory and its buffer
zones would ultimately be provided with CGI sheets. The Thrumshingla
National Park, with an area of 768 square kilometers, was established
in July 1998.
 |
| The
department of tourism (DoT) and the nature conservation division (NCD)
have identified two trekking routes in western central and central Bhutan
as part of pilot project to develop community tourism in the country. The
two trekking routes will form the basis of a study on developing a proper
framework for community based tourism in consultation with the primary
stakeholders or the community members themselves. |
|
Community based tourism
is an approach where the local community is actively involved in its development
and management, are able to derive benefits and enhance income, and promote
conservation of nature and culture.
| 'Vision
and strategies' for protected areas |
 |
Bhutan
today has five national parks (Royal Manas National Park, Jigme Dorji National
Park, Black Mountains National Park, Thrumshingla National Park, Wangchuck Centennial Park), four
wildlife sanctuaries (Bomdeling Wildlife Sanctuary, Sakteng Wildlife
Sanctuary Khaling/Neoli Wildlife Sanctuary, Jigme Khesar Strict Nature Reserve (former Toorsa Strict Nature Reserve))
and a nature reserve which make up about 26 percent of the country's area.
Apart from several endangered species of flora and fauna, 7,000 species
of plants, 165 species of mammals and 700 species of birds can be found
in the forests of Bhutan which cover 72 percent of the country's area.
 |
|
A Bengal tiger was sighted at the Thrumshingla N.P., 3,000 metres a.s.l.
|
| Two
years ago a 'biological corridor' was created to link the protected areas
to prevent the 'genetic erosion' of plants and animals. Conservation
of the natural environment has always been a priority of the royal government.
The new vision and strategy document, he said, will ensure a more focused
approach and also take into account emerging conservation issues in the
management of the protected areas. |
|
The
document, among other things, will set conservation goals, give direction
and incorporate the changing role of the nature conservation division.
While lack of adequate communication among various stakeholders, human
wild life conflicts, poaching, inadequate human and financial resources
and forest fires have been identified as major problems, the richness of
biodiversity, strong political donor support, potential for eco-tourism
and research opportunities are outlined as opportunities. Although a protected
area system was established since the early 60's most of the areas were
confined to the northern and southern belts.
Apart
from several endangered species of flora and fauna, 7,000 species of plants,
165 species of mammals and 700 species of birds can be found in the forests
of Bhutan which cover 72 percent of the country's area.
| Thrumshingla
National Park: Rhododendron garden opened |
 |
 |
A
rhododendron garden has opened at the Thrumshingla National Park. The park
commemorate the International Year of Mountains 2002.
|
 |
The
Thrumshingla National Park is situated between Jakar und Mongar.
According
to the ministry of agriculture the garden, to be formally known as "In
Situ Rhododendron Garden", will "showcase" Bhutan's rhododendron diversity
in their natural habitat. The development of the garden, 22 hectares in
area and containing 22 different species of rhododendron, is part of a
series of activities being undertaken by the royal government to commemorate
the international year of mountains.
Out of 46 known species of rhododendrons
in Bhutan four - R. kesangiae, R. pogonophyllum, R. bhutanense and R. flinckii - are endemic to the kingdom. Among its numerous ethno-botanical value,
rhododendrons are used to make incense, traditional medicines (to treat
dysentery, rheumatism, diarrhoea and sciatica), for carving (traditional
wooden containers), as natural insecticide and to make agricultural implements.
top
|
Dead firs are living homes
|
 |
|
Park officials hold firm against pressure from locals to exploit forest wealth
|
Dead Or Alive: What appears desolate is actually a habitat rich in biodiversity
Dense fogs and gloom cast by colossal mountains covered in thick forest that surround the area give travellers ascending the country's highest pass, Thrumshingla, from the base of Sengor between Trashigang and Bumthang, an eerie feeling.
The first thing travellers notice, as the fog clears on drawing near the top of the pass, are the giant scarred dead fir trees that stick out among the many pine trees, locals call dhungshing, which they said existed for more than 400 years.
 |
| The
department of tourism (DoT) and the nature conservation division (NCD)
have identified two trekking routes in western central and central Bhutan
as part of pilot project to develop community tourism in the country. The
two trekking routes will form the basis of a study on developing a proper
framework for community based tourism in consultation with the primary
stakeholders or the community members themselves. Community based tourism
is an approach where the local community is actively involved in its development
and management, are able to derive benefits and enhance income, and promote
conservation of nature and culture. |
|
Today, park officials and villagers are at loggerheads. The former insist that these dead trees be saved, as they are habitat to numerous species of birds and animals; while villagers want to cut them off for use, which in turn would allow these trees to grow anew.
Residents of some 230 households under Ura gewog, who have been using these fir trees for construction purposes before the park was established in 1998, approached the park officials to allow them to use the trees over the last four years.
Ura Makrong's 55 households even submitted a petition to the agriculture minister to allow the use of the resources, which were at their disposal until it was protected under the park.
Thrumshingla park officials and Ura villagers are caught in a debate over whether to use or save fir trees
"The DPT coordinator, who took our petition to the minister, told us that the minister had approved it," a resident said. "But we're still restricted from using them."
Makrong tshogpa Karma said that timber from one fir tree was equivalent to 40 or 50 pine trees. "This could help in conserving more trees and nature," he said.
 |
|
Besides their dark texture, he said, locals preferred fir trees for their endurance against withering that came with time.
"The trees are dying anyway," an Ura resident said. "The park should let us use it, instead of watching them go to waste."
Locals said the fir trees grew anew once the dead ones were felled. "We have been living here all our lives and actually watched that process," a senior resident said. "Once they die, there is regeneration."
|
|
But park officials argue that, although the fir trees were dead, they were home to many endangered birds and animals.
"The areas in the Khadopang and Geyzamchu, about 21 km from Ura, are habitats of red panda, blood pheasant, mono pheasant and serow," park officials said.
They were adamant about sparing even a single tree as they fell in the centre zone of the restricted area. "The nature conservation rules of the country forbid use of any resources from strictly restricted areas," a park official said.
Opposing the local belief that felling dead fir trees allowed new ones to grow, park officials said regeneration was impossible if they were disturbed.
"We allow local residents to use fir trees from identified buffer zones," park officials said. "It's not that we are restricting them totally."
 |
| Contributed
by Tashi Dema , Kuensel, Bhutan's National Newspaper, May 2010 |
top
| Animals in Bhutan |
 |
| Information on Bhutan |
 |
top
| Links |
 |
 |
 |
External
Links |
|













