|
Nepal National Parks Chitwan |
|
|
 |
| Protected
Areas and World Heritage: Chitwan National Park |
 |
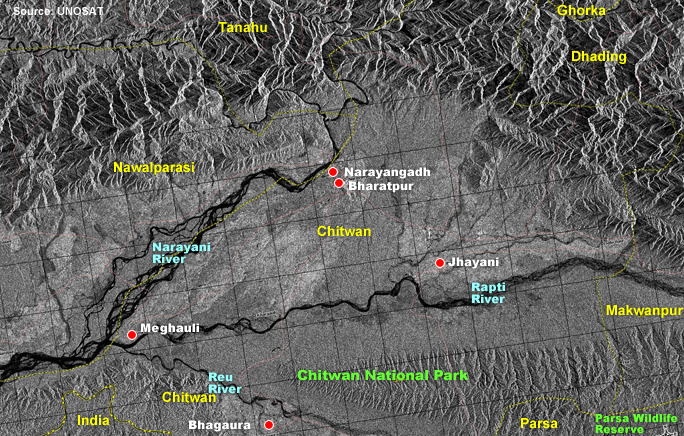
Chitwan
lies in the lowlands or Inner Terai of southern central Nepal on the international
border with India. The park's boundaries extend from the Dauney Hills on
the west bank of the Narayani River eastward 78km to Hasta and Dhoram
rivers. The park is bounded to the north by the Narayani and Rapti rivers
and to the south by the Panchnad and Reu rivers and a forest road. 27°20-27°40'N,
83°52'-84°45'E
 |
| Parsa
Wildlife Reserve is contiguous to the eastern boundary of the park and
extends as far eastwards as the Bheraha and Bagali rivers. 27°15'-27°35'N,
84°45'-84°58'E
Chitwan
was declared a national park in 1973, following approval by the late
King Mahendra in December 1970. The bye-laws (Chitw an National Park Regulations)
were introduced on 4 March 1974. Substantial additions were made to the
park in 1977 and the adjacent Parsa Wildlife Reserve was established in
1984. The habitat had been well protected as a royal hunting reserve from
1846 to 1951 during the Rana regime. |
|
An area south of the Rapti River was first proposed as a rhinoceros sanctuary in 1958 , demarcated in 1963
and later incorporated into the national park. Chitwan
was inscribed on the World Heritage List in 1984.
Chitwan
was enlarged from 54,400ha to its present size of 93,200ha in 1977. Parsa
Wildlife Reserve covers 49,900ha. There was a proposal to further enlarge
the protected areas complex by establishing the 25,900ha Bara Hunting Reserve,
adjacent to and east of Parsa Wildlife Reserve, but this has been
dropped.
| Information
on Nepal's Himalayas |
 |
|