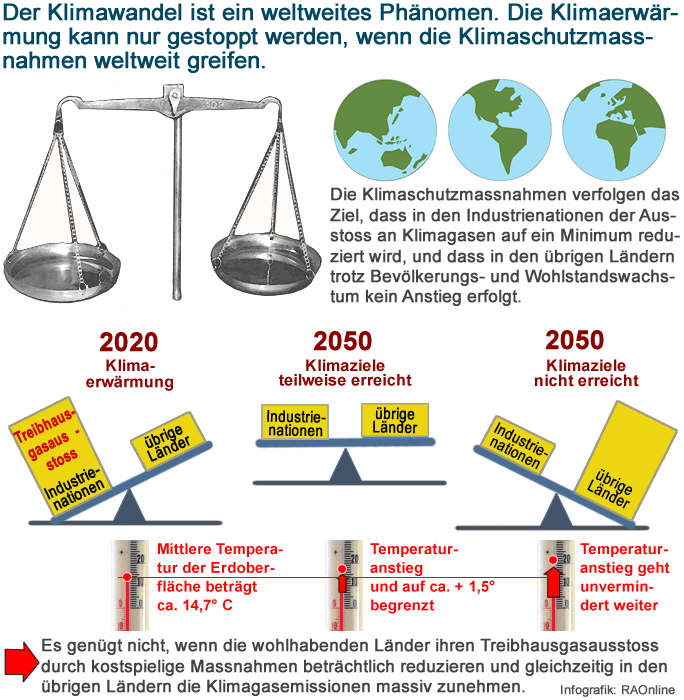
| Klimawandel - Climate Change |
 |
Klimakonferenz-COP27 Sharm el-Sheik 2022 |
 |
NGOs über COP27 |
 |
COP: Weitere Informationen |
 |
Klimawandel Weitere Informationen |
|
|
| UNO Klimakonferenz COP27 in Sharm el-Sheik (Ägypten) 2022 |
 |
| Die Weltklimakonferenz COP27 fand vom 11. November 2022 bis zum 20. November 2022 in Sharm el-Sheik (Ägypten) statt. |
| Die Weltklimakonferenz COP (UN Framework Convention on Climate Change Conference of the Parties) ist die grösste zwischenstaatliche Konferenz für Klimafragen. |
|
| UNO-Klimakonferenz COP27: Ziele nicht ganz erreicht |
 |
Die 27. Klimakonferenz (COP27) in Sharm el-Sheik ist am 20. November 2022 zu Ende gegangen. Wichtige Themen waren die Verabschiedung eines Arbeitsprogramms für den Klimaschutz und Lösungen für den Umgang mit Schäden, die durch den Klimawandel entstehen. Die Staaten haben sich auf ein Arbeitsprogramm bis 2026 geeinigt. Dieses nimmt jedoch die Länder mit dem grössten Treibhausgasausstoss nicht ausdrücklich in die Pflicht. Die Schweiz bedauert diesen Entscheid und wird sich dafür einsetzen, dass auch diese Länder ihren Beitrag leisten. Für die verletzlichsten Länder wurde ein neuer Fonds beschlossen, der sie im Umgang mit Schäden durch den Klimawandel unterstützt. Die Schweiz begrüsst die zusätzliche Hilfe grundsätzlich. Zentrale Fragen rund um den Fonds müssen aber noch geklärt werden.
| Source: Text Bundesamt für Umwelt BAFU, 25. 20. November 2022 |
 |
| COP27 Reaches Breakthrough Agreement on New "Loss and Damage" Fund for Vulnerable Countries |
 |
The United Nations Climate Change Conference COP27 closed today with a breakthrough agreement to provide "loss and damage" funding for vulnerable countries hit hard by climate disasters.
"This outcome moves us forward," said Simon Stiell, UN Climate Change Executive Secretary. "We have determined a way forward on a decades-long conversation on funding for loss and damage – deliberating over how we address the impacts on communities whose lives and livelihoods have been ruined by the very worst impacts of climate change."
Set against a difficult geopolitical backdrop, COP27 resulted in countries delivering a package of decisions that reaffirmed their commitment to limit global temperature rise to 1.5 degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels. The package also strengthened action by countries to cut greenhouse gas emissions and adapt to the inevitable impacts of climate change, as well as boosting the support of finance, technology and capacity building needed by developing countries.
Creating a specific fund for loss and damage marked an important point of progress, with the issue added to the official agenda and adopted for the first time at COP27.
Governments took the ground-breaking decision to establish new funding arrangements, as well as a dedicated fund, to assist developing countries in responding to loss and damage. Governments also agreed to establish a ‘transitional committee’ to make recommendations on how to operationalize both the new funding arrangements and the fund at COP28 next year. The first meeting of the transitional committee is expected to take place before the end of March 2023.
Parties also agreed on the institutional arrangements to operationalize the Santiago Network for Loss and Damage, to catalyze technical assistance to developing countries that are particularly vulnerable to the adverse effects of climate change.
COP27 saw significant progress on adaptation, with governments agreeing on the way to move forward on the Global Goal on Adaptation, which will conclude at COP28 and inform the first Global Stocktake, improving resilience amongst the most vulnerable. New pledges, totaling more than USD 230 million, were made to the Adaptation Fund at COP27. These pledges will help many more vulnerable communities adapt to climate change through concrete adaptation solutions.COP27 President Sameh Shoukry announced the Sharm el-Sheikh Adaptation Agenda, enhancing resilience for people living in the most climate-vulnerable communities by 2030. UN Climate Change’s Standing Committee on Finance was requested to prepare a report on doubling adaptation finance for consideration at COP28 next year.
The cover decision, known as the Sharm el-Sheikh Implementation Plan, highlights that a global transformation to a low-carbon economy is expected to require investments of at least USD 4-6 trillion a year. Delivering such funding will require a swift and comprehensive transformation of the financial system and its structures and processes, engaging governments, central banks, commercial banks, institutional investors and other financial actors.
Serious concern was expressed that the goal of developed country Parties to mobilize jointly USD 100 billion per year by 2020 has not yet been met, with developed countries urged to meet the goal, and multilateral development banks and international financial institutions called on to mobilize climate finance.
At COP27, deliberations continued on setting a ‘new collective quantified goal on climate finance’ in 2024, taking into account the needs and priorities of developing countries.
"In this text we have been given reassurances that there is no room for backsliding," said Stiell. "It gives the key political signals that indicate the phasedown of all fossil fuels is happening."
The World Leaders Summit, held over two days during the first week of the conference, convened six high-level roundtable discussions. The discussions highlighted solutions – on themes including food security, vulnerable communities and just transition – to chart a path to overcome climate challenges and how to provide the finance, resources and tools to effectively deliver climate action at scale.
COP27 brought together more than 45,000 participants to share ideas, solutions, and build partnerships and coalitions. Indigenous peoples, local communities, cities and civil society, including youth and children, showcased how they are addressing climate change and shared how it impacts their lives.
The decisions taken here today also reemphasize the critical importance of empowering all stakeholders to engage in climate action; in particular through the five-year action plan on Action for Climate Empowerment and the intermediate review of the Gender Action Plan. These outcomes will allow all Parties to work together to address imbalances in participation and provide stakeholders with the tools required to drive greater and more inclusive climate action at all levels.
Young people in particular were given greater prominence at COP27, with UN Climate Change’s Executive Secretary promising to urge governments to not just listen to the solutions put forward by young people, but to incorporate those solutions in decision and policy making. Young people made their voices heard through the first-of-its-kind pavilion for children and youth, as well as the first-ever youth-led Climate Forum.
In parallel with the formal negotiations, the Global Climate Action space at COP27 provided a platform for governments, businesses and civil society to collaborate and showcase their real-world climate solutions. The UN Climate Change High-Level Champions held a two-week programme of more than 50 events. This included a number of major African-led initiatives to cut emissions and build climate resilience, and significant work on the mobilization of finance.
"We have a series of milestones ahead. We must pull together, with resolve, through all processes, may they be national, regional, or others such as the G20. Every single milestone matters and builds momentum," said Stiell. "The next step for change is just around the corner, with the United Arab Emirates’ stewardship of the First Global Stocktake. For the very first time we will take stock of the implementation of the Paris Agreement. It will independently evaluate the progress we have made and if our goals are adequate. It will inform what everybody, every single day, everywhere in the world, needs to do, to avert the climate crisis."
Stiell reminded delegates in the closing plenary that the world is in a critical decade for climate action. A stark report from UN Climate Change underpinned his remarks, as well as discussions throughout the two-week conference. According to the report, implementation of current pledges by national governments put the world on track for a 2.5°C warmer world by the end of the century. The UN’s Intergovernmental Panel on Climate Change indicates that greenhouse gas emissions must decline 45% by 2030 to limit global warming to 1.5°C.
COP27 President Sameh Shoukry said: "The work that we’ve managed to do here in the past two weeks, and the results we have together achieved, are a testament to our collective will, as a community of nations, to voice a clear message that rings loudly today, here in this room and around the world: that multilateral diplomacy still works…. despite the difficulties and challenges of our times, the divergence of views, level of ambition or apprehension, we remain committed to the fight against climate change…. we rose to the occasion, upheld our responsibilities and undertook the important decisive political decisions that millions around the world expect from us."
Speaking about the year ahead, Stiell said UN Climate Change will help Parties and future COP Presidencies to navigate this path to the new phase of implementation.
A summary of some of the other key outcomes of COP27 follows below.
Technology
COP27 saw the launch of a new five-year work program at COP27 to promote climate technology solutions in developing countries.
Mitigation
COP27 significantly advanced the work on mitigation. A mitigation work programme was launched in Sharm el-Sheikh, aimed at urgently scaling up mitigation ambition and implementation. The work programme will start immediately following COP27 and continue until 2030, with at least two global dialogues held each year. Governments were also requested to revisit and strengthen the 2030 targets in their national climate plans by the end of 2023, as well as accelerate efforts to phasedown unabated coal power and phase-out inefficient fossil fuel subsidies.
The decision text recognizes that the unprecedented global energy crisis underlines the urgency to rapidly transform energy systems to be more secure, reliable, and resilient, by accelerating clean and just transitions to renewable energy during this critical decade of action.
Global Stocktake
Delegates at the UN Climate Change Conference COP27 wrapped up the second technical dialogue of the first global stocktake, a mechanism to raise ambition under the Paris Agreement. The UN Secretary-General will convene a ‘climate ambition summit’ in 2023, ahead of the conclusion of the stocktake at COP28 next year.
Snapshot of other announcements
The conference heard many announcements:
Countries launched a package of 25 new collaborative actions in five key areas: power, road transport, steel, hydrogen and agriculture.
UN Secretary-General António Guterres announced a USD 3.1 billion plan to ensure everyone on the planet is protected by early warning systems within the next five years.
The UN Secretary-General’s High-Level Expert Group on Net-Zero Commitments published a report at COP27, serving as a how-to guide to ensure credible, accountable net-zero pledges by industry, financial institutions, cities and regions.
A G7-led plan called the Global Shield Financing Facility was launched at COP27 to provide funding to countries suffering climate disasters.
Announcing a total of USD 105.6 million in new funding, Denmark, Finland, Germany, Ireland, Slovenia, Sweden, Switzerland, and the Walloon Region of Belgium, stressed the need for even more support for the Global Environment Facility funds targeting the immediate climate adaptation needs of low-lying and low-income states.
The new Indonesia Just Energy Transition Partnership, announced at the G20 Summit held in parallel with COP27, will mobilize USD 20 billion over the next three to five years to accelerate a just energy transition.
Important progress was made on forest protection with the launch of the Forest and Climate Leaders’ Partnership, which aims to unite action by governments, businesses and community leaders to halt forest loss and land degradation by 2030.
About the UNFCCC
With 197 Parties, the United Nations Framework Convention on Climate Change (UNFCCC) has near universal membership and is the parent treaty of the 2015 Paris Climate Change Agreement. The main aim of the Paris Agreement is to keep a global average temperature rise this century well below 2 Celsius and to drive efforts to limit the temperature increase even further to 1.5 degrees Celsius above pre-industrial levels. The UNFCCC is also the parent treaty of the 1997 Kyoto Protocol. The ultimate objective of all agreements under the UNFCCC is to stabilize greenhouse gas concentrations in the atmosphere at a level that will prevent dangerous human interference with the climate system, in a time frame which allows ecosystems to adapt naturally and enables sustainable development.
| Source: Text UNFCCC, 20 November 2022 |
 |
| Klimakonferenz-COP10
Buenos Aires 2004 |
| COP10:
Ein Sachgeschäft - Brandrodungen verschlimmern Treibhauseffekt |
 |
Die
Zerstörung des brasilianischen Regenwaldes durch Brandrodungen
ist hauptverantwortlich für die schädlichen Gasemissionen des
südamerikanischen Landes, die den so genannten Treibhauseffekt
verursachen. Das geht aus einer Regierungsstudie aus den Jahren 1990 bis
1994 hervor, die in Brasilien erstmals veröffentlicht wurde. Die Studie
wird auch bei der UNO-Klimakonferenz COP10 vorgestellt.
Nach
der in Brasilia veröffentlichten Studie war das grösste Land
Lateinamerikas zwischen 1990 und 1994 für drei Prozent aller weltweiten
Treibhaus-Gasemissionen verantwortlich. Als überraschend werteten
Experten die Tatsache, dass die Brandrodungen zur Vorbereitung von Anbauflächen
im Urwald 1994 für drei Viertel aller Treibhausgasemissionen in Brasilien
sorgten. Die Verbrennung fossiler Brennstoffe hatte nur einen Anteil von
23 Prozent.
Der
brasilianische Ausstoss von Kohlendioxid (CO2), jenes Gases, das für
den Treibhauseffekt und die globale Temperaturerhöhung hauptverantwortlich
ist, erhöhte sich laut der Studie allein zwischen 1990 und 1994 um
fünf Prozent auf 1,03 Milliarden Tonnen.
Brasiliens
Regierung versicherte, dass sie tue alles, um die Zerstörung des Regenwaldes
zu bremsen. Dazu müssten vor allem die illegalen Aktivitäten
bekämpft werden, sagte sie.
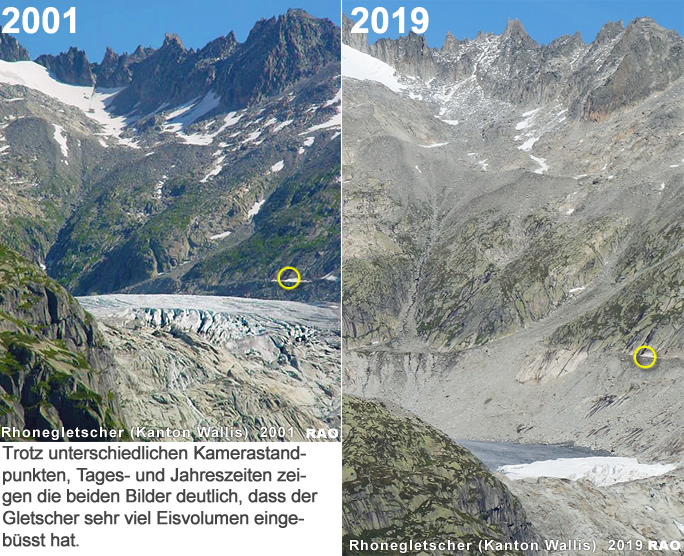
| vor 12 Jahren bis 17 Jahren |
Bereits zu Beginn des neuen Jahrtausends ud frpüher warnten die Klimawissenschaftler eindringlich vor den Folgen des Klimawandels. Ende 2019 wissen wir, ihre Voraussagen sind mehrheitlich nachprüfbar eingetroffen. Die Warnrufe der Wissenschaft sind nicht verstummt. Im Gegenteil! Seit 20 Jahren wird das Konsum- und Freizeitverhalten derart "gepuscht", wie wenn die Folgen des Klimawandels weiterhin Fiktion bleiben würden.
| Schlagzeilen 2003 - 2007 |
 |
| Vorbote
der Klimazukunft |
2003 |
|
| Unbeständigkeit nimmt zu |
2003 |
|
| Es
braucht eine langfristige Politik |
2004 |
|
|
| Klimakrise näher denn je |
2004 |
|
| Klimaänderung so rasant wie noch nie |
2005 |
|
| Es wird heiss in Europa |
2005 |
|
|
|